Repair of Sucker Rods
In order to meet the needs of oil companies in high-quality equipment and increase profitability of production by the Ocher Machine-building Plant, a method for deep repair of sucker rods was developed. A sucker rod recovered by the deep repair method successfully underwent the pilot testing.
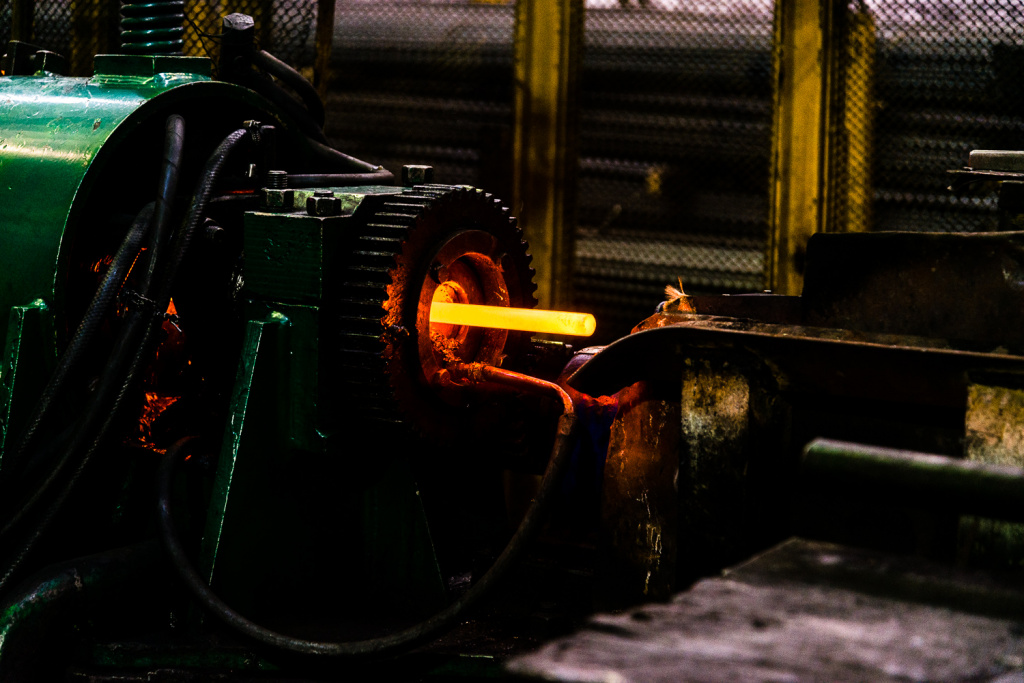
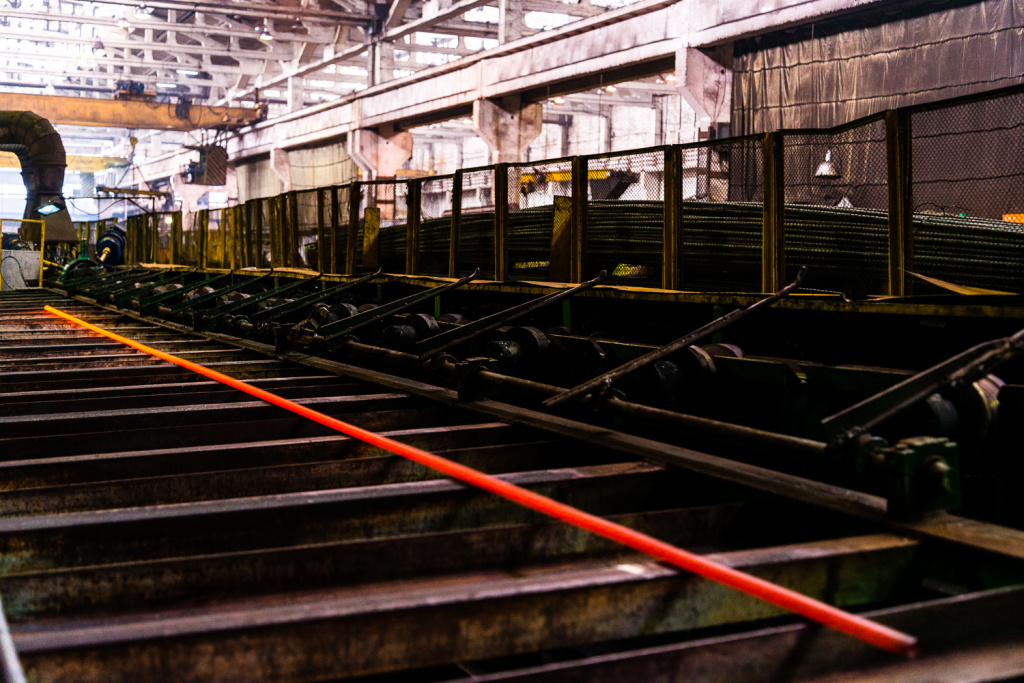
The deep repair method is based on the principle of hot radial-displacement rolling of a ШН 7/8” post-consumer rod (22 mm) not subject to repair, to ШН 3/4" (19 mm) due to reduction of the diameter of the cross-section of a rod body. The rolling temperature is 1150±15°С on the area of section and along the length of the rod. One of the peculiarities of this process is the final compression of the surface and adjacent layers in the direction of metal outflow, which allows to obtain a high-quality surface with a high level of the special strength and plasticity properties. The process of radial-displacement rolling of a post-consumer sucker rod allows to obtain fine-grained structure of the blank and to distribute the carbide constituent evenly into a metal.
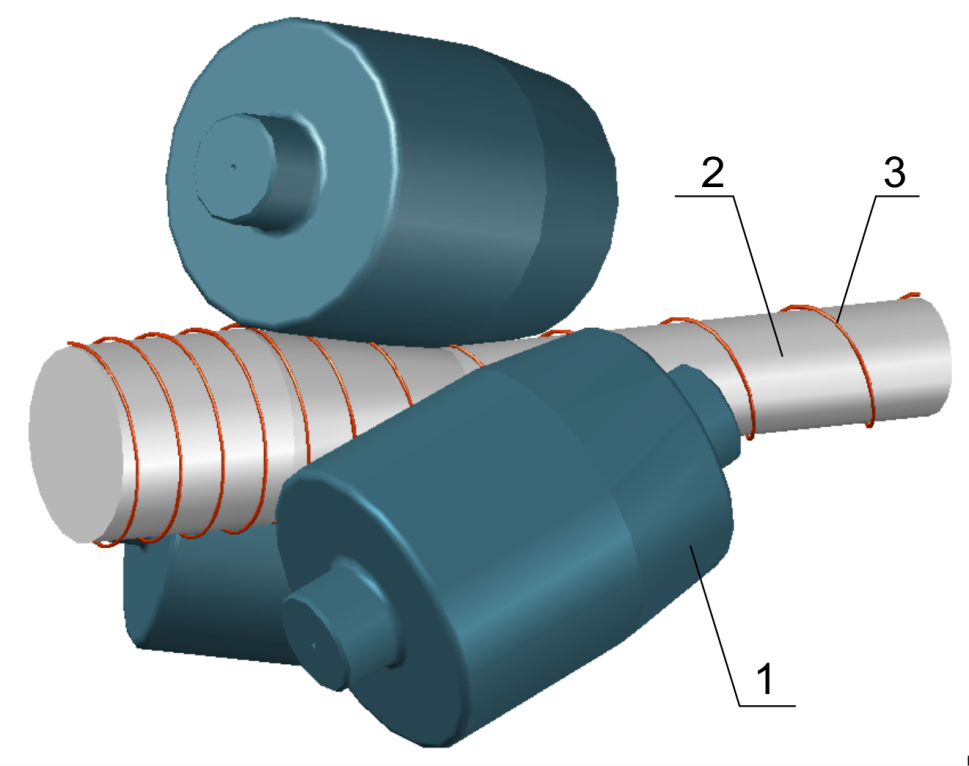
Figure 1. Radial-displacement rolling pattern. 1 – roller; 2 – blank; 3 – motion trajectory of a metal on the surface of a blank.
The method is based on the trajectory control of the motion of a deformable metal. In the deformation zone, helial outflow of a metal is created with the braking of the outer layer of a blank and the acceleration of the internal layer. Multidirectional flows cause intense displacement in the roll stock. The refinement of the structural configuration is intensified manyfold. The metal acquires the characteristic finely divided structure, which is practically not available for other stationary metal forming methods (Figure 2). In terms of its morphology, structure and properties, a metal after radial-displacement rolling becomes a material of new quality. Both physical-mechanical and service properties of the metal are improved and stabilized at a level above the traditional one.
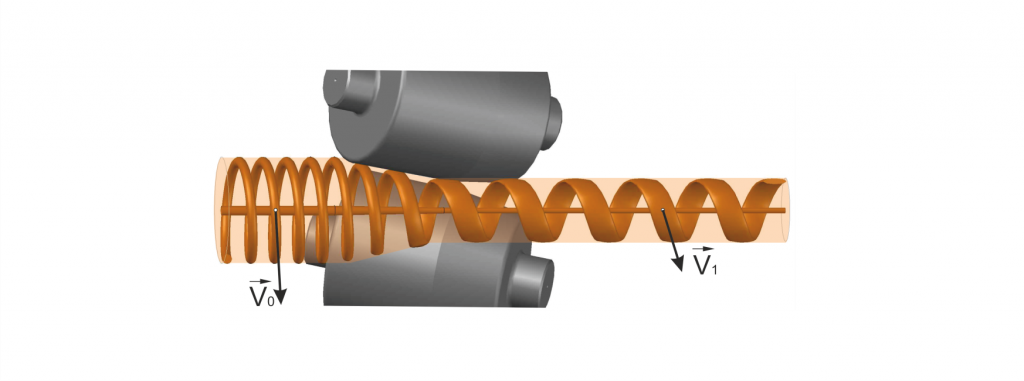
Figure 2. Flow pattern of the outer layer of a blank. V0(1) are the velocity of a metal before and after the deformation zone.
The bodies of processed sucker rods are usually affected by surface defects. As a result of the trajectory-controlled radial-displacement rolling, the velocity of the peripheral layers of the blank reduces, which is connected with the formation of expanding tubes of current (diffusers) (Fig. 2). This type of flow produces dissipative (sprayer-type) effect on structural elements, which take the form of isotropic isolated particles with high dispersity. In the same way, surface discontinuities, dissipated, intensively decrease in their development. Recrystallization and diffusion processes, which remove the operating fatigue of the rods, are intensified. In addition, the discrete-continuous character of the process actively contributes to the elimination of defects and obtaining of high-precision rolled products. Each element of the blank surface, being in continuous spiral motion, is repeatedly processed by rollers. The deviation of the diameter of the rods from the nominal does not exceed 1%.
The article on this technology was published in the journal Inzhenernaya Praktika No. 9/2014




